International Satellite System for Search and Rescue
The Mission of the Cospas-Sarsat is to provide search and rescue services with accurate, timely and reliable information about the detected danger signal emitted by the danger transmitter ELT, EPIRB and PLB operating at a frequency of 406MHz through satellite and terrestrial components of the system.
The genesis of Cospas-Sarsat Programme starts on 29 November 1979 in Leningrad (now St. Petersburg). France, Canada, the Soviet Union and the United States signed the first cooperation agreement, ratified in 1980, integrating the national systems into one, the international Cospas-Sarsat system, enabling more efficient use of all active satellites to receive signals of danger, sent at a frequency of 121.5 MHz and 406 MHz, anywhere in the world.
Tests conducted in the years 1982-1984 confirms adopted in the planning capabilities of the system, declaring the system operational readiness. On October 5, 1984, the, France, Canada, the Soviet Union and the United States signed a second cooperation agreement, and thus, at the first meeting of the Cospas-Sarsat committee in July 1985, Cospas-Sarsat system has been declared fully operational.
In 1988, France, Canada, the Soviet Union and the United States signed the third agreement on cooperation in the framework of the Cospas-Sarsat system. The Agreement constitutes the essence of Cospas-Sarsat Programme, providing financial guarantees and operational continuity of the system and the availability of on equal terms and conditions for all countries.

COSPAS-SARSAT: General principles of operation
In an emergency situation, activated emergency transmitter emits a signal at a emergency frequency of 406MHz (1). Distress signal is received by the satellites of the Cospas-Sarsat (2) and transmitted to the ground system components - LUT (3). Then, the received distress signal is sent to the Mission Control Center System - MCC (4) and Search and Rescue Co-ordination Centres - RCC (5), which initiates the start of search and rescue, whose mission is to help people who are in distress.
On 31 May 2005, in Warsaw, President of the Civil Aviation Authority, (authorized by Resolution of the Council of Ministers No 107/2005 of 25 April 2005) signed a Memo of the Polish Accession Programme for International COSPAS-SARSAT as a user (Polish Monitor 2006 , No. 13, item. 171), which is the contractor.
According to the government's Statement of 30 December 2005 on the binding of the Polish accession to the Note Program of the International COSPAS-SARSAT as a user, signed in Warsaw on 31 May 2005 (Polish Monitor of 2006 No. 13, item. 172 ), Poland on September 16, 2005, is a full-fledged member of the Cospas-Sarsat Programme.
The main tasks of the Civil Aviation Authority, under the Polish membership in the Cospas-Sarsat Programme:
- keeping records of board and personal danger signal transmitter ELT, EPIRB and PLB 406MHz and the transmission of the information contained in the records to the Aeronautical Rescue Coordination Centre – ARCC Warsaw”;
- development of the annual report of the Cospas-Sarsat system evaluation elements;
- cooperation with the Secretariat of the Cospas-Sarsat Programme;
- supervision of the Polish Air Navigation Services Agency (SPOC Poland) in cooperation with the Cospas-Sarsat Mission Control Center System - CMC Moscow;
- implementation and supervision of the application in Poland, adopted by the Cospas-Sarsat Programme coding danger protocols signal transmitters;
- coordinate testing a danger signal transmitters, as recommended and approved by the Cospas-Sarsat Programme procedure, published in document C / S S. 007 "Handbook of Beacon Regulations" and on the website of the Civil Aviation Authority;
- monitor the proper use of a danger signal transmitters registered in Poland;
- cooperation with the Polish Air Navigation Services Agency, ARCC Warsaw and Maritime Search and Rescue Service in matters of Cospas-Sarsat Programme.
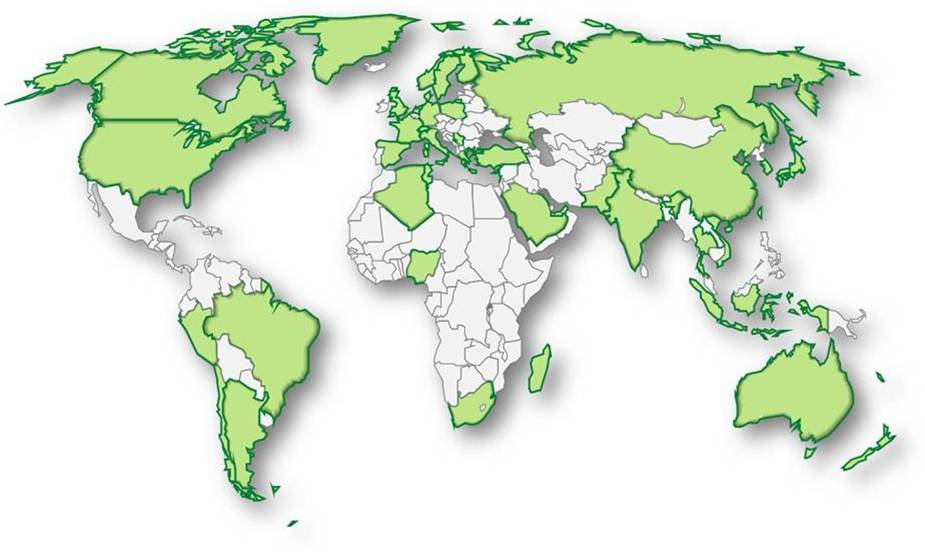
Currently, the Cospas-Sarsat Programme includes 43 member states.
Ground Component working for the benefit of the system consists of 58 LEOLUT terminals, 21 GELOLUT terminals and 31 MCC and satellite component working for the benefit of the system contains: 6 LEOSAR satellites and six GEOSAR satellites.
The Council of the International Cospas-Sarsat Programme decided that from 1 February 2009, a satellite monitoring system does not scan the danger signals emitted by the danger signal transmitters at a frequency of 121.5MHz.
Nevertheless, the frequency of 121.5MHz, in accordance with international Standards and Recommended Practices contained in Annex 10 on aeronautical telecommunications to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, signed at Chicago on 7 December 1944, is still emergency frequency. The frequency of 121.5MHz using a search-and-rescue aircraft, leading the way search-government at the time of search and rescue.
The future of Cospas-Sarsat Programme is MEOSAR satellite system consisting of a constellation of satellites: the American GPS, European Galileo and the Russian Glonass, characterized by a larger and continuous coverage area of the globe, than satellites LEOSAR. Slower movement of the satellites MEOSAR can receive several signals sent by a transmitter danger signal during one satellite pass, which allows much more precise location of the distress signal transmitter.
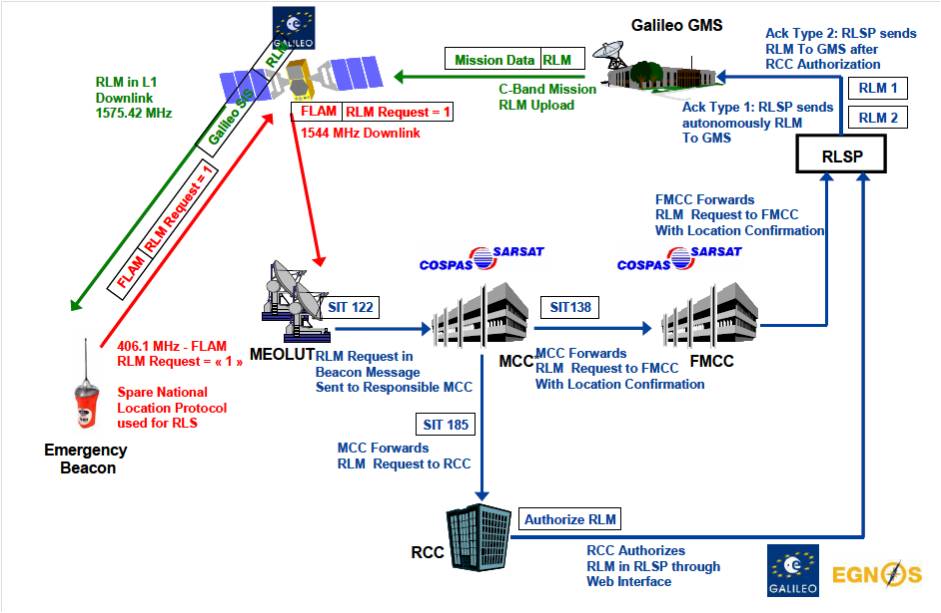
The future of Cospas-Sarsat Programme is also the Return Link Service function, used only in the European satellite navigation system Galileo, which will be available with a danger signal transmitters second generation. The Return Link Service is based on submission by the terrestrial component of the feedback system, a danger signal to the transmitter that generates a signal of danger, as an acknowledgment of receipt of a danger signal from the Cospas-Sarsat system satellites.